Protein Supplement
Sep 17, 2020
Hydroxyapatite extraction from dry fish scales

Admin
Admin
What is Hydroxyapatite? (HA)
Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite. As its name suggests, it is the hydroxylated representative of phosphate minerals known as apatites [chemical formula: Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2]. It is a calcium phosphate similar to the bone mineral in composition. It forms the mineral part of bone and matrix of teeth. It is responsible for the inherent rigidity of the bones and teeth.
With the advent of nanotechnology, production of nanomaterials has gained considerable attention especially when biomaterials are involved. Nano-hydroxyapatite (nano-HAp), is largely attracting interest as a biomaterial for use in prosthetic applications, considering its similarity with the human hard tissue in terms of chemical composition, size and crystallography.
Properties
Bio-compatibility, Biodegradability
Osteogenic capacity, Osteoconductivity
Inert, Non-toxic and Non-inflammatory
Applications
Bone tissue engineering (bone repair, bone regeneration)
Bone void fillers for orthopedic, traumatology, spine, maxillofacial and dental surgery.
Orthopedic implants (bone graft/filler) and dental implant coating
Dentin hypersensitivity in periodontitis
Promotes enamel remineralization
Restoration of periodontal defects
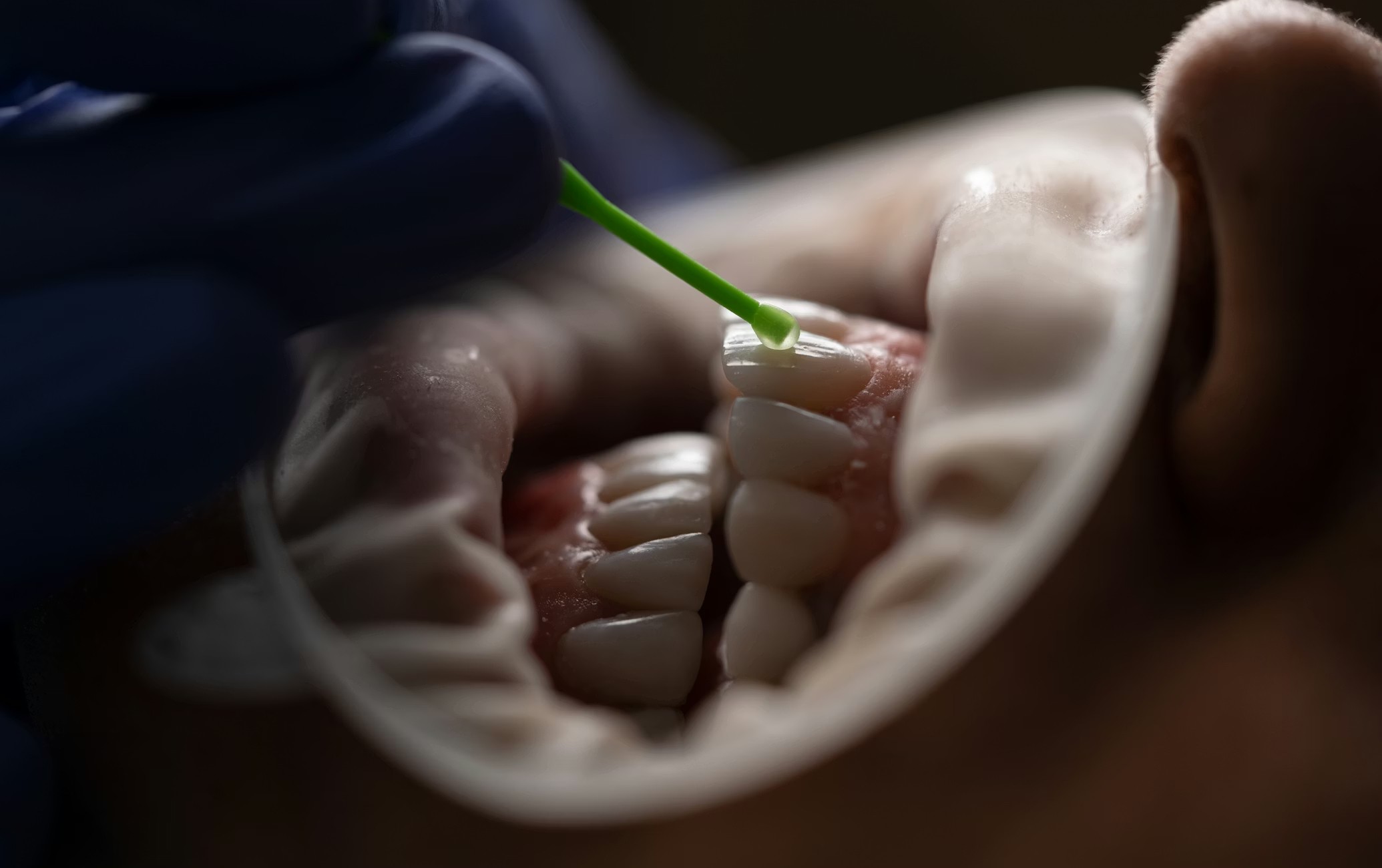
Medical use
Hydroxylapatite (HA) is used as coating on Titanium and stainless steel implants to reduce the implant rejection rate by mimicking the body. It can also be used in instances of bone voids or defects.
By virtue of its bioactivity, it encourages the bone to grow and restores the defect. It promotes increased gap healing between bone and hydroxyapatite, shortens bone healing at the bone-implant interface and inhibits corrosion. These advantages are prompting manufacturers to replace conventional titanium plasma spray coatings with nano-hydroxyapatite coatings.
Oral care use
Nano-hydroxyapatite forms 97% of enamel, it gives an appearance of bright white and eliminates the diffuse reflectivity of light by closing the small pores of the enamel surface. To treat dentin hypersensitivity (enamel erosion), synthetic nano-hydroxyapatite gets deposited in the defects and mimics natural enamel apatite. This property of nano-hydroxyapatite has led to its use in toothpastes and mouth-rinsing solutions to promote restoration of demineralized enamel or dentin surface.
Fishes as source of Hydroxyapatite
Hydroxylapatite (HA) can be chemically synthesized in a laboratory or obtained from naturally occurring biological sources viz. coral, bovine or marine fishes. Synthesis of HA from fish is largely being explored, since the last few years. Fish bone and scales are considered as an alternative to synthetic and bovine hydroxylapatite (HA), due to low manufacturing cost and safety concerns. Fish sources have also been demonstrated to present low risks of disease transmission as compared to bovine sources.
Further, abundant availability of fish in the environment will ensure consistent supply to manufacturers, thereby addressing any supply constraints.
This bio-medical use of fish waste/by-products i.e. bone and scales is also an incredible advantage to humans, for reducing environmental pollution and threats of biohazards and aiding waste management. Fish species such as Salmon, Carp, Japanese anchovy, Sardine, Tilefish, Tuna have been used to obtain hydroxylapatite (HA).
Extraction method
Many studies are published investigating the extraction process using various techniques viz. Calcination and Alkaline hydrolysis. Calcination method is a simple, cheap and effective method to extract hydroxylapatite (HA). Fish bones are boiled in water to remove adherent fish meat. Then they are dried at room temperature and calcinated in a furnace at about 600-950 °C. These are then milled into fine powders for use. The time and temperature for calcination is being researched for obtaining hydroxylapatite (HA).
In a nutshell, Hydroxyapatite is a component of human hard tissue viz. bones and teeth. Aging global population and growing demand for bioactive ceramics in the bone replacement surgeries and dental surgery will be key factors in fueling market growth for hydroxyapatite in orthopedic and dental applications. Also, with advancement of research and exploration of fishes as potential sources of HA, the market for hydroxyapatite is sure to grow.
What is Hydroxyapatite? (HA)
Hydroxyapatite, also called hydroxylapatite (HA), is a naturally occurring mineral form of calcium apatite. As its name suggests, it is the hydroxylated representative of phosphate minerals known as apatites [chemical formula: Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2]. It is a calcium phosphate similar to the bone mineral in composition. It forms the mineral part of bone and matrix of teeth. It is responsible for the inherent rigidity of the bones and teeth.
With the advent of nanotechnology, production of nanomaterials has gained considerable attention especially when biomaterials are involved. Nano-hydroxyapatite (nano-HAp), is largely attracting interest as a biomaterial for use in prosthetic applications, considering its similarity with the human hard tissue in terms of chemical composition, size and crystallography.
Properties
Bio-compatibility, Biodegradability
Osteogenic capacity, Osteoconductivity
Inert, Non-toxic and Non-inflammatory
Applications
Bone tissue engineering (bone repair, bone regeneration)
Bone void fillers for orthopedic, traumatology, spine, maxillofacial and dental surgery.
Orthopedic implants (bone graft/filler) and dental implant coating
Dentin hypersensitivity in periodontitis
Promotes enamel remineralization
Restoration of periodontal defects

Medical use
Hydroxylapatite (HA) is used as coating on Titanium and stainless steel implants to reduce the implant rejection rate by mimicking the body. It can also be used in instances of bone voids or defects.
By virtue of its bioactivity, it encourages the bone to grow and restores the defect. It promotes increased gap healing between bone and hydroxyapatite, shortens bone healing at the bone-implant interface and inhibits corrosion. These advantages are prompting manufacturers to replace conventional titanium plasma spray coatings with nano-hydroxyapatite coatings.
Oral care use
Nano-hydroxyapatite forms 97% of enamel, it gives an appearance of bright white and eliminates the diffuse reflectivity of light by closing the small pores of the enamel surface. To treat dentin hypersensitivity (enamel erosion), synthetic nano-hydroxyapatite gets deposited in the defects and mimics natural enamel apatite. This property of nano-hydroxyapatite has led to its use in toothpastes and mouth-rinsing solutions to promote restoration of demineralized enamel or dentin surface.
Fishes as source of Hydroxyapatite
Hydroxylapatite (HA) can be chemically synthesized in a laboratory or obtained from naturally occurring biological sources viz. coral, bovine or marine fishes. Synthesis of HA from fish is largely being explored, since the last few years. Fish bone and scales are considered as an alternative to synthetic and bovine hydroxylapatite (HA), due to low manufacturing cost and safety concerns. Fish sources have also been demonstrated to present low risks of disease transmission as compared to bovine sources.
Further, abundant availability of fish in the environment will ensure consistent supply to manufacturers, thereby addressing any supply constraints.
This bio-medical use of fish waste/by-products i.e. bone and scales is also an incredible advantage to humans, for reducing environmental pollution and threats of biohazards and aiding waste management. Fish species such as Salmon, Carp, Japanese anchovy, Sardine, Tilefish, Tuna have been used to obtain hydroxylapatite (HA).
Extraction method
Many studies are published investigating the extraction process using various techniques viz. Calcination and Alkaline hydrolysis. Calcination method is a simple, cheap and effective method to extract hydroxylapatite (HA). Fish bones are boiled in water to remove adherent fish meat. Then they are dried at room temperature and calcinated in a furnace at about 600-950 °C. These are then milled into fine powders for use. The time and temperature for calcination is being researched for obtaining hydroxylapatite (HA).
In a nutshell, Hydroxyapatite is a component of human hard tissue viz. bones and teeth. Aging global population and growing demand for bioactive ceramics in the bone replacement surgeries and dental surgery will be key factors in fueling market growth for hydroxyapatite in orthopedic and dental applications. Also, with advancement of research and exploration of fishes as potential sources of HA, the market for hydroxyapatite is sure to grow.
Related Blogs
Whatever we produce,
We must fully use
Contact Us
Phone No:
022 4924 0706
+91 9730007882
Location:
923, IJMIMA complex, MDP Road, Malad West, Mumbai – 400064, Maharashtra, India.
71/17, Topsia Road, (South) Near Millat Nagar Masjid, Kolkata: 700046, West Bengal, India.
© 2026 Nizona Marine Products Private Limited. All Rights Reserved.
Whatever we produce,
We must fully use
Contact Us
Phone No:
022 4924 0706
+91 9730007882
Location:
923, IJMIMA complex, MDP Road, Malad West, Mumbai – 400064, Maharashtra, India.
71/17, Topsia Road, (South) Near Millat Nagar Masjid, Kolkata: 700046, West Bengal, India.
© 2026 Nizona Marine Products Private Limited. All Rights Reserved.
Whatever we produce,
We must fully use
Contact Us
Phone No:
022 4924 0706
+91 9730007882
Location:
923, IJMIMA complex, MDP Road, Malad West, Mumbai – 400064, Maharashtra, India.
71/17, Topsia Road, (South) Near Millat Nagar Masjid, Kolkata: 700046, West Bengal, India.
© 2026 Nizona Marine Products Private Limited. All Rights Reserved.



































