Unfortunately for us, our natural production of collagen declines as we age, which means we can afford to get more from an outside source. While we often think of wellness in terms of what we can see and apply on the outside, there’s a lot that can, and should, happen on the inside. People are more aware of germs and staying healthy now than ever before. What we eat and what supplements we take are absolutely essential to creating a strong and stable immune system. Collagen may help with strengthening the connective tissues, improving digestive tract and gut health, increasing bone health, joint health, and more. Clearly, collagen’s benefits, especially helping with the gut and digestive track, are important for staying healthy. The healing of digestive tract and repairing connective tissues is helpful for defending from harmful bacteria.
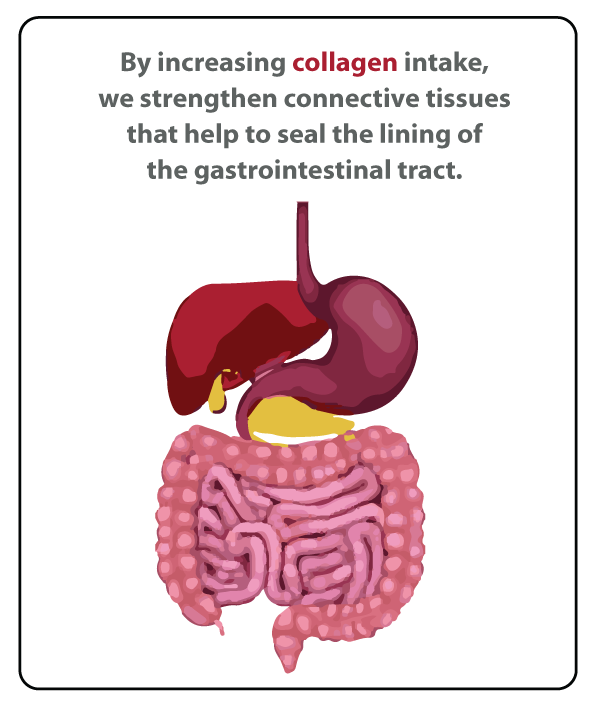
Collagen helps to strengthen our gut lining. Having a weak gut lining allows for bad bacteria to more easily enter our system. By increasing collagen intake, we strengthen connective tissues that help to seal the lining of the gastrointestinal tract. Because the amino acids in collagen build the tissues that line the colon and GI tract, collagen may help treat or prevent gastrointestinal disorders and related issues like mal-absorption of nutrients, autoimmunity, eczema, fatigue, brain fog and more.

Thank you for your reading. Join the conversation by posting a comment.